- Muhammad Akbar1, Hasil Khan2, Alamdar Hussain , Sujjad Hyder1, Farida Begum1, Mayoor Khan3, Anwar Ali2, Syed Arif Hussian4, Ghulam Raza1 Sher Wali Khan4, Qamar Abbas4, Salar Ali1
- Department of Environmental Sciences Karakoram International University Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan
- Forest Education Division Pakistan Forest Institute, Peshawar, Pakistan
- Wildlife Conservation Society near Serina Hotel Jutial Gilgit, Pakistan
- Department of Biological Sciences Karakoram International University Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan
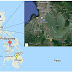
The current study was carried out in Chilghoza forest of Goharabad District Diamer. The study area is situated in the foothills of Hindukush mountain range at 5 Km from KKH, at an elevation of 2000 to 5000 m with an area of 310 km².
Six stands of Chilghoza Forest were selected randomly for the enumeration of data from different locations and aspects suing Point Center Quadrate Method. Stand densities of the six stands were 16.61, 12.168, 7.367, 7.163, 4.320, 3.982 m²/ha respectively in all six stands.
The distribution of Pinus gerardiana is satisfactory in almost in all the stands however the distribution of associated species were very poor. The poor distribution and gaps in small size middle and in large classes, Juniperus excelsa and Quercus ilex seem to be losing ground in this forest due to anthropogenic activities i.e. felling, grazing, sliding, burning and several human induced factors.
As the study area falls under the category of private forest, thus it was found that all of the respondents were owners of the forest. It was interesting to know that the Chilghoza forests are exclusively used for nuts collection. It was found that 100% villagers depend on the Chilghoza forest for nuts collection and no timber or fuel wood collection is made from the Chilghoza forests, conservation committee have imposed fine on cutting of Chilghoza forests for fuel wood or timber. However, the associated tree species including Juiper , Oak, Birch and Blue pine are felled for fuel wood and other wood purposes. Government and non-governmental organizations should come forward to support local communities in conservation of the valuable Chilghoza forests.
Full Article Available at: Volume 5, Number 5, November 2014 – JBES
Journal Name: Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES)


















0 comments:
Post a Comment